What is CI/CD Pipeline in DevOps
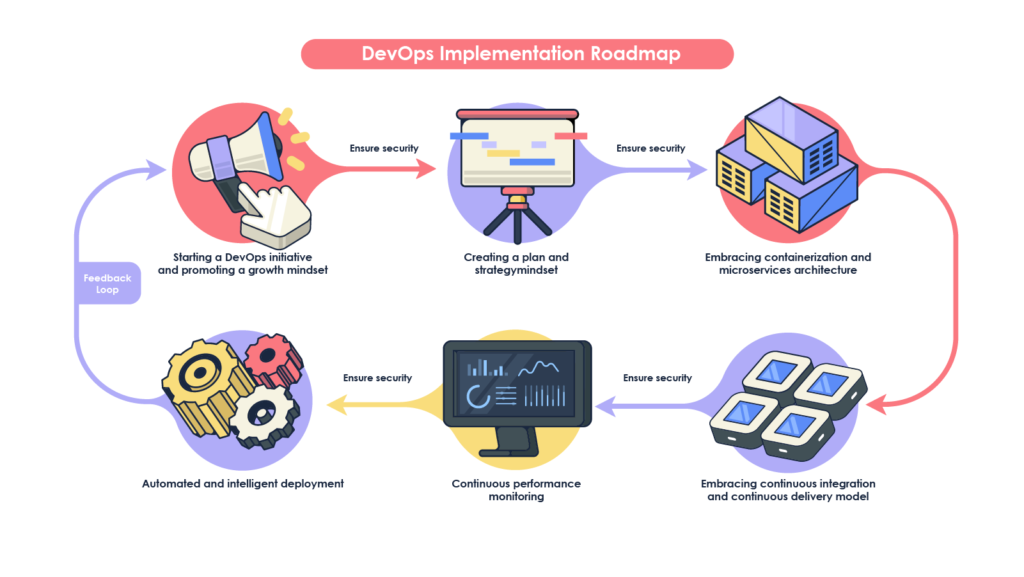
DevOps is evolving rapidly and has become one of the demanding skillsets for developers who like automation and make a successful career in the software development field. Cloud is the new oil for companies and now every company is regarded as a software company, hence, the cloud has become not an option anymore but a must to be factor. DevOps being the center of the software development today, CI/CD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery) approach makes most of the things easy.
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD is a practice in DevOps that allows developers to quickly and automatically test, package, and deploy their applications. Most commonly, it is often achieved by leveraging a server called Jenkins, which serves as the most common CI/CD orchestrator. Jenkins listens to specific inputs given by the developer and, when triggered, kicks off a pipeline flow.
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development method in which the developers’ code gets integrated several times a day. Whenever a developer checks-in the code, each time the change is verified by an automated pipeline(server) and gives early feedback, in case if there are any bugs.
Continuous Delivery (CD) comes after CI and it is the ability to introduce changes with every commit, making the code ready for production so that it can be deployed to production on demand and as a routine activity. Code changes can be like new features, bug fixes, updates, configuration changes, etc. One important thing to note here is to ensure safety checks, so the bugs get detected before they get promoted to the production.
What is a pipeline?
A pipeline consists of code written by development and, in some cases, operations teams, too, to instruct tools like Jenkins which actions to take during the CI/CD pipeline process. This pipeline is often goes through something like building the code, testing the code, and if the tests pass, deploy the application to the various environments like development, test, or production environment.
A pipeline is a series of events or jobs that happen in a flow in the software delivery pipeline from start to the end.
The pipeline can be visualized as a sequence of stages shown below:
What are the benefits of CI/CD?
- Improved developer efficiency
- Faster time to market
- Faster software builds
- Improved collaboration between the teams
- Easy to find and fix bugs
- High-quality code
Things to consider while building a CI/CD pipeline
- Peer code review
An honest peer code reviews play a vital role in the pipeline.
For a piece of feature functionality to be set as complete, it requires the developer to have another developer do the code review and check thoroughly for any disturbances in the code. Group code reviews also work amazingly well, but it doesn’t scale when there are many developers contributing a large amount of code. Peer code review can happen easily and the lead of the team should make sure this is followed by all within the team. One important dimension to do this is to catch bugs before they get into production or to the end-user.
- Build in a containerized environment
For easy pipeline configuration, using tools like Docker is a must because it creates an environment that supports the pipeline in all aspects of creating, packaging and shipping your application. It also helps in debugging the specific container if something goes wrong instead of checking the whole pipeline. One important thing is to have separate containers for each build from the beginning and they’re really easy to implement too.
- Shorten the feedback loop
In order to shorten the feedback loop, run the quickest tests first in the testing suite. An example of a proper flow could be: code quality → unit tests → build → staging deployment → e2e test.
- Do CI first
Focus on implementing CI first. After the CI is proved to be stable and reliable, then only move on to set up the CD part. This gives confidence to developers and makes their work easy to go on to the next phase of implementing CD.
- Compare efficiency
After you implement monitoring, compare the productivity and velocity of the team before and after setting up the CI/CD pipeline. This will surely let you know if the new approach has improved the efficiency or any changes are required
- Insert security checkpoints in the pipeline
Shifting the focus of security to the far left is one of the important aspects of DevOps. Making sure security is every developer who checks-in the code is very important.
- Implement an easy way to rollback
One important part of a successful CI/CD pipeline is an easy, one-button click, option to rollback to previous changes/state in case if something goes wrong. Usually, this in many cases just means re-deploying a previous release to be on the safer side.
- Proactively monitor your CD pipeline
No matter how careful we are, sometimes a faulty algorithm, dependencies, or any unknown events can cause the software to behave unpredictably. It is very difficult to troubleshoot within the CD pipeline and debugging can be a nightmare and may not be even possible in a production environment. So, proactive monitoring throughout the pipeline is a great approach and a better way to catch any bugs or problems before they reach the production stage.
A good pipeline should always produce the same output for any given input, with no uncertainties in runtime. Any breakdowns, intermittent failures or slowdowns can create frustration among developers.
In the age of advanced cloud computing and ever-increasing complexity, CI/CD provides your team and the entire organization, the speed, and confidence it needs to deliver software to your customers reliably. CI/CD approach facilitates building great applications with more stability and faster time to market. Having good automation throughout allows for a more streamlined development pipeline, thus enabling developers to get the feedback more quicker, fix things fast, learn fast and build better, more consistent apps regularly.
Want to learn and build a career in DevOps?

Responses